Hair Loss – Causes, Treatments and Remedies
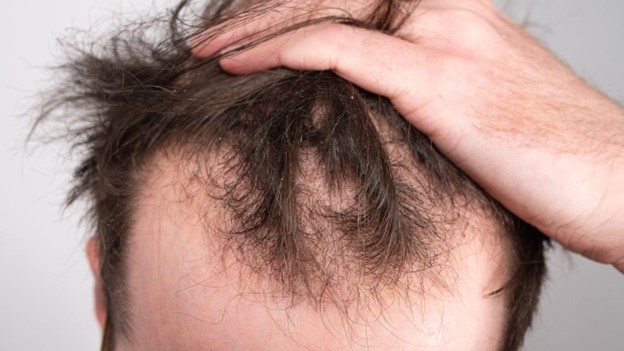
Hair loss is a normal part of the aging process for many men and women. However, for some it can be an indication of a serious health condition. If you are experiencing noticeable thinning or baldness, there are treatments that can help slow the progression of balding and even encourage partial regrowth.
Most people lose 50 to 100 hairs a day, usually without noticing. This is because each individual hair follicle goes through cycles of growth and rest, with some follicles producing new hair while others stop or regress. When a hair follicle stops producing, it falls out and is replaced by scar tissue. Normally, a hair follicle produces for 2 to 6 years before it goes into a permanent rest cycle. If the cycle is disrupted or if there is too much scar tissue, then the hair follicle may not grow back.
Patterned Hair Loss
The most common type of hair loss is hereditary patterned baldness in both men and women. This type of baldness typically starts in early adulthood and is caused by changes to hormones. In men, the hairline recedes while in women it gradually thins all over the scalp.
Hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth and menopause can also cause temporary or permanent hair loss. Other causes include medical conditions such as alopecia areata (al-o-PEE-she-uh ar-ee-A-tuh), which is an immune system disorder that causes patchy hair loss, scalp infections like ringworm, and a psychiatric disorder called trichotillomania (trik-o-til-o-MAY-nee-uh), which involves compulsive hair pulling. Medications, especially drugs used for chemotherapy to treat cancer, can also cause hair loss.
It is important to see your GP if you are concerned about your hair loss, particularly if it is sudden or accompanied by other symptoms. Your GP can help diagnose the problem and refer you for specialist treatment.
Can you Regrow Hair?
There are a number of treatments that can help promote hair growth and reduce hair loss, including minoxidil (Rogaine), which is available as an over-the-counter topical treatment. This works by reversing the effects of DHT on hair follicles and can be applied daily to the scalp.
Another option is a more invasive hair transplant, which can be carried out by either FUT or FUE. In FUT, a surgeon removes a strip of skin from the back of your scalp where there is still a lot of hair and then reinserts it into the area where you are losing your hair. In FUE, a surgeon transplants hair follicles directly to the bald areas of the scalp using a special tool.
Some people who are undergoing a hair transplant will also receive medication to stimulate regrowth such as finasteride (Propecia) or dutasteride (Avodart). In addition, some patients may be given antifungal medications to prevent the immune system from attacking healthy hair follicles, and spironolactone or estrogen for premenopausal women or post-menopausal women. In some cases, doctors may also prescribe a low-level steroid to reduce inflammation.
Should you wish to discuss your condition with an experienced Australian trained Doctor or expert in this area. Please book in for an online and Telehealth consultation. Phenix Health is always available when you need us 24/7. Contact bookings@phenixhealth.com.au.





Phenix Health delivers online health services 24/7 provided by Australian doctors and healthcare professionals.