
Endometriosis Treatment: Endometriosis is a chronic condition that can be painful, affect fertility, and lead to reduced participation in school, work and sporting activities. The condition is estimated to have cost $7.4 billion in Australia in 2017–18, mostly through reduced quality of life and productivity losses.
While 11% of Australian women suffer from endometriosis, conventional first-line treatment options remain inadequate for many. A recent survey conducted by researchers at the University of NSW confirms this, citing 72% of respondents reported using illicit cannabis to manage their symptoms
(Source Link: https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/can.2021.0116)
Endometriosis Treatment for Boosting Fertility
Endometriosis is associated with an increased risk of infertility and increased difficulty with falling pregnant. As a general rule, the greater the amount of endometriosis, the greater the risk of difficulties relating to fertility.
Surgery has been demonstrated to help women with mild endometriosis become more fertile. Although this hasn’t been established, treating more severe endometriosis with surgery appears to increase a woman’s fertility.
For surgical removal, laparoscopy (key-hole surgery) is the most commonly utilised procedure. Endometrioses may be excised (surgically removed) or destroyed (burned) using techniques called “ablation” and/or “fulguration”. Endometrial cysts in the ovaries are best treated surgically because they are unlikely to go away on their own, and cannot be treated with medications.
Other reasons for infertility should be investigated and addressed where possible.
Medicinal Cannabis – An Emerging Treatment Option
There are a variety of remedies now available that can either complement or replace current medical treatment options, including the use of medicinal cannabis.
Medicinal cannabis is an emerging treatment option for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain. In 2017, it became possible for Australian doctors to prescribe medicinal cannabis for chronic health conditions that did not respond adequately to first line treatments. As of October 2021, there have been over 180,000 approved applications for medicinal cannabis within Australia.
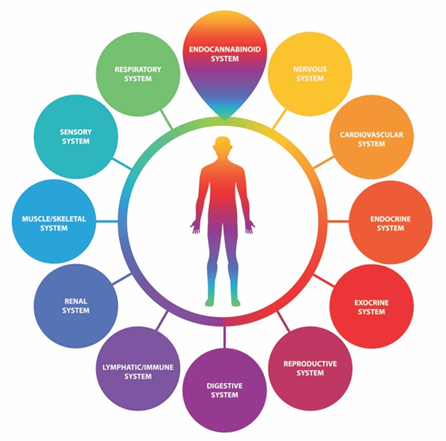
The Endocannabinoid System
Just like the circulatory and respiratory systems, every person has an Endocannabinoid System (ECS) within their body. The role of the ECS is to maintain homeostasis (balance). The ECS consists of endocannabinoids, endocannabinoid receptors, and enzymes.
Endocannabinoid receptors are abundant in the female reproductive organs, as well as the central and peripheral nervous systems, and the immune system. Endocannabinoids are produced by the body and interact with these receptors to influence our stress response, metabolism, appetite, mood and sleep, among other things.
What are Phytocannabinoids?
Phytocannabinoids are the plant-based cannabinoids found in medicinal cannabis. They mimic the body’s own endocannabinoids to influence our body systems and responses.
Cannabinoids have an influence over both physiological and pathophysiological functions of female reproduction, as well as affecting the pain and anxiety often associated with endometriosis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a powerful, non-psychoactive cannabinoid that can be used in a variety of ways to manage the symptoms of endometriosis.
CBD for Women’s Health
Cannabinoid receptors in the pelvis, ovaries, endometrium, vulva and the central and peripheral nervous systems influence inflammation, nociception, and arousal at these therapeutic targets. Cannabinoids trigger localised vasodilation and relaxation of pathological smooth muscle contraction and/or spasticity.
For these reasons, cannabinoids may be helpful in the management of chronic pelvic pain, endometriosis, dysmenorrhea (painful periods), vulvodynia, vaginismus, painful sex, as well as peri-menopausal and menopausal symptoms that include vaginal dryness and insomnia.
In addition to the management of chronic pain and inflammation, CBD has been used as an anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, anti-insomnia and neuroprotective agent. It is possible that while chronic pain is being managed with cannabinoid medicine, other areas of concern such as mental health conditions may also respond to medicinal cannabis treatment; improving a number of quality of life factors.
Conventional Treatment Options
Analgesics – for pain
Conventional treatments for the pain and inflammation associated with endometriosis include over-the-counter medications such as Paracetamol (Panadol) and Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatories (NSAIDs such as Aspirin / Nurofen).
Hormone Treatments
Hormone treatments such as The Pill work to suppress a woman’s regular menstrual cycle, which slows or stops the formation of endometriosis. Other hormone treatments may also be useful in lowering endometriosis-related discomfort, but some women may experience negative effects from these treatments.
Laparoscopy or keyhole surgery
Initially, laparoscopy may be provided to assist in the diagnosis, but may also be performed to diagnose and treat all visible endometriosis. This is accomplished with a laser or diathermy, which destroys the endometriosis. Endometriosis deposits may also be surgically removed.
Hysterectomy
More comprehensive surgery, such as hysterectomy and ovarian removal, may be considered in a limited proportion of women who have significant symptoms that are not resolved by medication or other surgical treatment.
Surgery on the intestines
Endometriosis can sometimes harm the intestinal wall. When this causes severe symptoms, it may be recommended that the afflicted section of bowel be removed. This would necessitate intestinal surgery, which is not a frequent procedure. If you’d like to secure a consultation with a qualified medicinal cannabis practitioner, please book here:





Phenix Health delivers online health services 24/7 provided by Australian doctors and healthcare professionals.